Top Inflammatory Foods in Your Diet and the Secret to Reducing Inflammation

Lets take a look at the top inflammatory foods and their impact on your well-being. In today's fast-paced world, our dietary choices play a crucial role in determining our health. In this article, we'll delve into the common ingredients that can trigger inflammation, identify the unsuspecting foods that harbor these culprits, explore how these ingredients wreak havoc on our bodies, and most importantly, discover the keys to embracing an anti-inflammatory diet. If you're in Phoenix, Arizona, we'll also touch upon local meal delivery services that can make this transition easier for you.
Unmasking Inflammatory Ingredients:
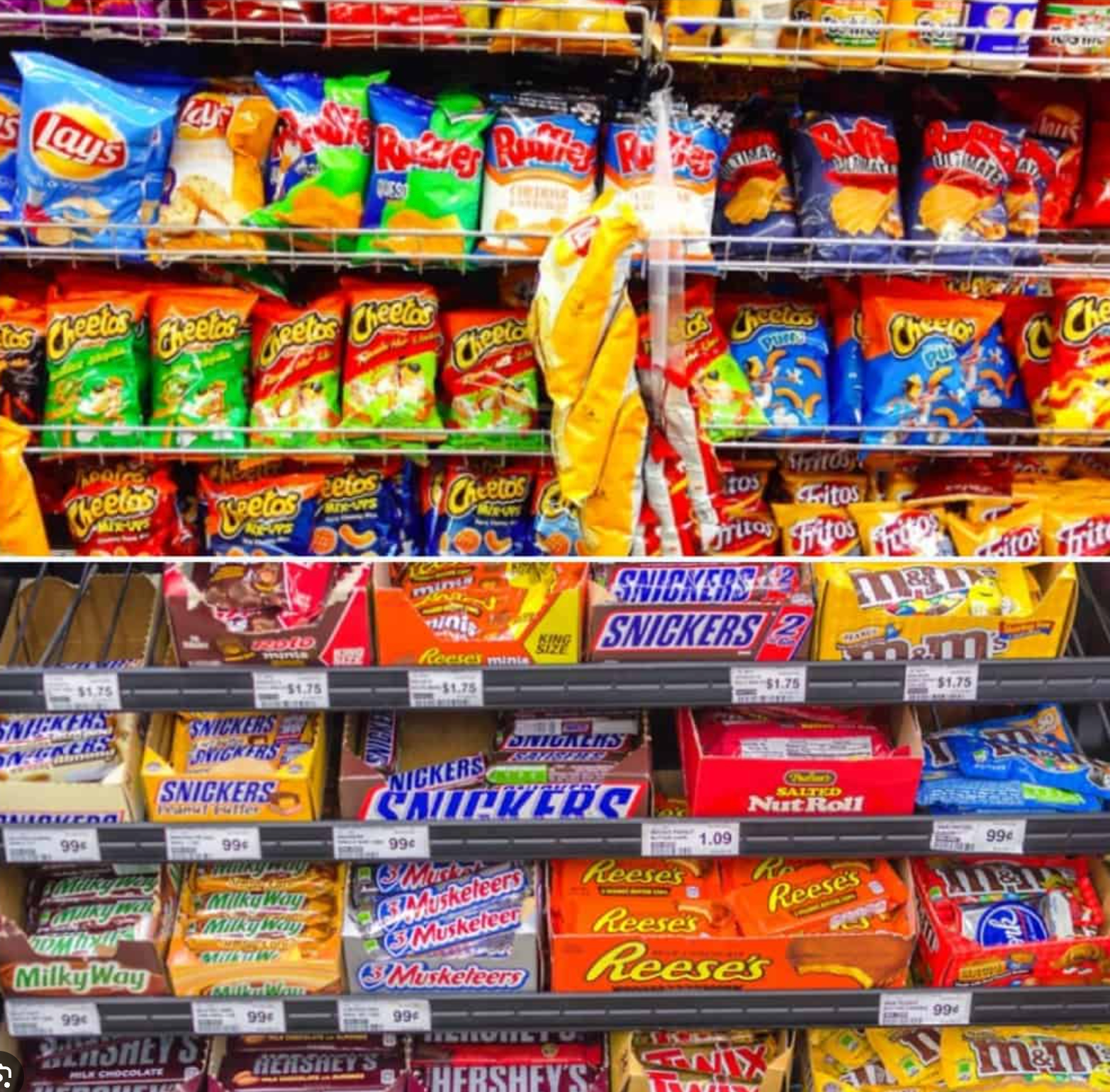
Inflammation can often be linked to the foods we consume daily. Certain ingredients have been identified as key instigators of inflammation, leading to a myriad of health issues. Local residents in Phoenix, Arizona, might unknowingly be incorporating these elements into their diets through common meals.
The Usual Suspects: Nothing that should surprise you.
- Refined Sugar: Found in numerous processed foods and beverages, refined sugar is a major culprit in causing inflammation.
- Trans Fats: Often present in fried and processed foods, trans fats are notorious for triggering inflammatory responses in the body.
- Refined Grains: Refined and enriched grains, commonly found in breads, pastas, and various processed food items, can contribute to inflammation due to several reasons:
- High Glycemic Index (GI): Refined grains have a higher glycemic index compared to whole grains. Foods with a high glycemic index can cause a rapid spike in blood sugar levels, leading to increased production of inflammatory markers in the body. This continuous cycle of blood sugar spikes and subsequent crashes can contribute to chronic low-grade inflammation.
- Reduced Fiber Content: During the refining process, the outer bran and germ layers of grains, which contain fiber and many beneficial nutrients, are often removed. Fiber plays a crucial role in regulating blood sugar levels and promoting a healthy gut microbiome. The lack of fiber in refined grains can contribute to an imbalance in the gut, potentially leading to inflammation.
- Nutrient Stripping: The refining process removes a significant portion of essential nutrients present in whole grains, such as vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. Enrichment is a process that adds back some of these nutrients, but often not in the same proportions or quality as they exist in whole grains. The loss of these nutrients can contribute to systemic inflammation.
- Pro-Inflammatory Fats: Some processed and refined grain products may contain unhealthy fats, such as trans fats and omega-6 fatty acids in excess. These fats have been linked to increased inflammation and may contribute to chronic inflammatory conditions when consumed in large quantities.
- Disruption of Gut Microbiota: Refined grains may alter the composition of the gut microbiota, leading to an imbalance that can contribute to inflammation. The gut microbiota plays a crucial role in immune function and overall health, and disruptions in its balance have been associated with inflammatory conditions.
- Artificial Additives: Preservatives, colorings, and flavor enhancers found in many packaged foods can contribute to inflammation.
- Artificial Sweeteners:
- Aspartame: Found in many diet sodas and sugar-free products, aspartame has been linked to inflammation and may cause adverse reactions in some individuals.
- Artificial Colorings:
- Tartrazine (Yellow 5), Red 40, Blue 1: These artificial colorings are often used in processed foods, candies, and beverages. Some studies suggest a potential link between artificial colorings and inflammatory responses.
- Artificial Flavor Enhancers:
- Monosodium Glutamate (MSG): Commonly used to enhance the flavor of savory dishes, MSG has been associated with inflammation and may cause symptoms like headaches and nausea in sensitive individuals.
- Preservatives:
- Sodium Nitrate/Nitrite: Often used in processed meats like bacon and hot dogs, these preservatives may contribute to inflammation and have been linked to certain health risks.
- BHA (Butylated Hydroxyanisole) and BHT (Butylated Hydroxytoluene):
- These synthetic antioxidants are used to prevent the oxidation of fats in processed foods. Some studies suggest that they may have inflammatory effects and pose health concerns.
- Thickeners like Guar Gum and Xanthan Gum
- Xanthan and Guar Gums have been associated with digestive issues, such as gas, bloating, and diarrhea, particularly in individuals with pre-existing digestive conditions. These digestive discomforts can indirectly contribute to inflammation in the gut for susceptible individuals.
How Inflammatory Ingredients Affect Your Body:
Understanding the mechanisms behind inflammation is essential. These ingredients can disrupt the delicate balance in your gut, leading to a cascade of reactions that manifest as inflammation. This inflammation, if chronic, has been linked to various health issues, from digestive problems to more severe conditions.
Recognizing Inflammation: Signs and Symptoms
Before we explore the solution, it's crucial to recognize when inflammation is occurring. Symptoms can vary but may include:
- Persistent fatigue
- Joint pain
- Digestive issues
- Skin problems
- Weight gain
The Anti-Inflammatory Diet: Your Path to Wellness
Now that we've identified the problem, let's explore the solution—an anti-inflammatory diet. Incorporating foods known for their anti-inflammatory properties can help restore balance in your body.
Top Anti-Inflammatory Foods:
- Fatty Fish: Rich in omega-3 fatty acids, salmon, mackerel, and sardines are potent anti-inflammatory foods.
- Leafy Greens: Kale, spinach, and collard greens are packed with antioxidants that combat inflammation.
- Berries: Blueberries, strawberries, and raspberries contain anti-inflammatory compounds that promote overall health.
Substituting Inflammatory Ingredients:
Making small changes in your diet can yield significant results. Swap out inflammatory ingredients with healthier alternatives:
- Choose Whole Grains: Opt for whole grains instead of refined ones to reduce inflammation.
- Healthy Fats: Incorporate olive oil, avocados, and nuts as alternatives to trans fats. Cut out all seed oils from your diet!
- Natural Sweeteners: Use honey or maple syrup instead of refined sugar for a healthier sweetness.
Your Journey to a Healthier You
As we conclude our exploration of inflammatory foods, the key takeaway is that small changes in your diet can lead to significant improvements in your well-being. Embracing an anti-inflammatory diet not only alleviates current health issues but also acts as a preventive measure for the future.
Ready to make a positive change in your diet? Explore the convenience of local meal prep delivery services in Phoenix, Arizona. Our services prioritize your health, offering delicious and nutritious meals tailored to an anti-inflammatory lifestyle. Contact us today to start your journey to a healthier you.
Remember, the power to reduce inflammation is in your hands, one mindful meal at a time. Check our our Signature meal plan here.